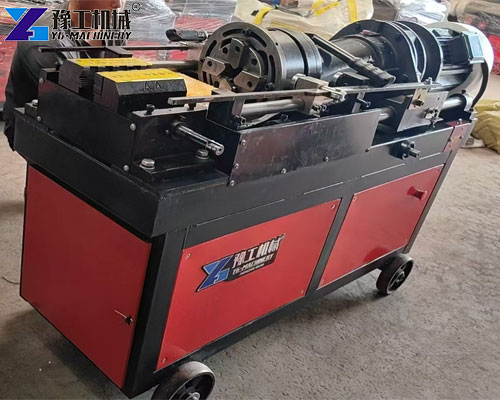
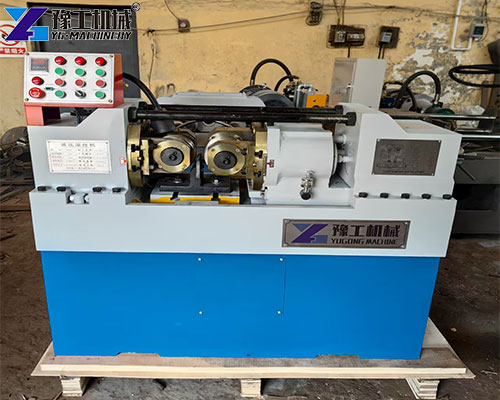


Thread rolling is a cold forming metalworking process used to create external threads by displacing material rather than cutting it away. Instead of removing metal, it uses hardened dies to plastically deform the surface of a cylindrical workpiece, forming precise and durable threads.
Because no material is removed, it produces threads with higher strength, improved fatigue resistance, and better surface finish compared to traditional thread cutting methods.
Related post: Steel bar straight thread rolling machine hydraulic [high efficiency]
24-hour hotline: +8613837115193
How Does Thread Rolling Work?
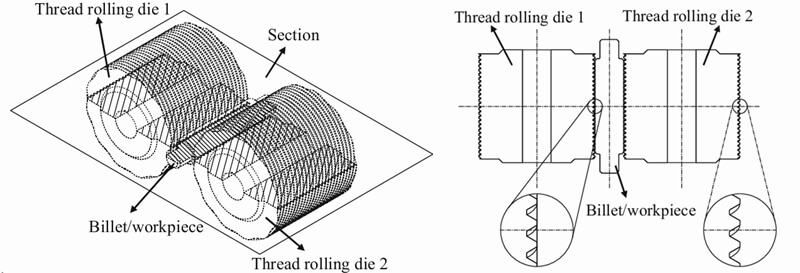
Unlike cutting, grinding, or chasing, the thread rolling process relies on high-pressure contact between the workpiece and rolling dies.
During operation:
- The workpiece is pressed between two or three hardened steel dies
- The dies rotate and force the material to flow into the thread profile
- Threads are formed as a mirror image of the die geometry
- The process occurs at room temperature (cold working)
Because the metal fibers follow the thread contour, the final threads are denser, smoother, and mechanically stronger.
Key Characteristics of the Thread Rolling Process
It is considered a high-efficiency, non-cutting manufacturing method, offering several inherent advantages:
- No chip generation or material waste
- Improved surface hardness due to cold working
- Excellent dimensional consistency
- Suitable for mass production
- Energy-efficient and environmentally friendly
These characteristics make it ideal for industries requiring high-strength threaded components.
Materials Suitable for Thread Rolling
Not all metals can be rolled successfully. Material selection plays a critical role in achieving high-quality threads.
Recommended Material Properties
A material is generally suitable for it if it meets the following conditions:
- Elongation ≥ 12%
- Good ductility and toughness
- High fatigue resistance
- Adequate compressive strength
- Good surface formability
Commonly Rolled Materials
- Low and medium carbon steels
- Alloy steels (annealed condition)
- Stainless steel (select grades)
- Aluminum alloys
- Copper and brass
Formability Index Rule:
Softer and more ductile materials are easier to roll, while very hard or brittle materials are better suited for thread cutting.

Thread Rolling vs. Thread Cutting
Thread rolling and thread cutting are both widely used, but they serve different manufacturing needs.
Advantages of Thread Rolling
- Higher thread strength
- Superior surface finish
- Longer tool life
- Faster cycle times
- Lower cost in high-volume production
Advantages of Thread Cutting
- Suitable for very hard materials
- Greater flexibility for small batches
- Can produce internal threads
- Compatible with larger or irregular stock
Choosing between rolling and cutting depends on material type, production volume, and performance requirements.
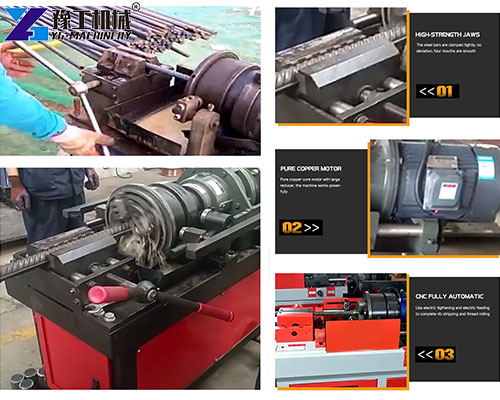


Typical Thread Rolling Applications
It components are widely used across multiple industries due to their strength and reliability.
Common applications include:
- Fasteners (bolts, screws, studs)
- Automotive components
- Aerospace parts
- Oil and gas fittings
- Medical device components
- Plumbing connectors
- HVAC system parts
- Industrial machinery assemblies
These applications benefit from the enhanced fatigue life and dimensional accuracy provided by rolled threads.
Mexican customer feedback after using our thread rolling machine
Why Thread Rolling Improves Thread Strength
One of the most important advantages of it is grain flow continuity.
During rolling:
- Metal fibers are compressed and aligned along the thread profile
- Surface hardness increases due to cold work
- Stress concentration at thread roots is reduced
As a result, rolled threads often exhibit higher tensile strength and longer service life than cut threads made from the same material.
Summary
Thread rolling is a high-efficiency cold forming process that produces strong, precise, and durable external threads without removing material. By improving grain structure and surface integrity, it offers significant advantages in performance, cost, and sustainability—especially in high-volume manufacturing.
For applications where strength, consistency, and fatigue resistance matter, thread rolling remains one of the most effective thread-forming technologies available.




